焼きなまし法(Simulated Annealing)と2-Opt法による巡回セールスマン問題の解法
巡回セールスマン問題とは
巡回セールスマン問題 (Traveling Salesman Problem; TSP)とは、複数の点(本来は都市)が与えられたときに、それらの点全てを通り、一周する経路の中で最短のものを求めるというものです。経路の数は $n!$ なので(スタート点を決めれば $(n-1)!$になりますが)、$n$が大きいとき、総当たりで求めると計算量が莫大になります。そこで効率よく近似解を求めるアルゴリズムが必要となるのです。
Demo
先に下のシミュレータの使い方を説明しておきます。まず画面をクリックして点をプロットします。もし直したい場合は 画面上の点を消去 またはc を押してください。次に 最短経路を計算 またはEnter を押せば最短経路が計算されます。計算が終了すれば、それまでで最も経路長が短い解が出力されます。なお、ハイパーパラメータは反復(Iteration)の回数を200, 開始時の温度(temp)を100にしています。
最適化手法
2-Opt法
今回のプログラムでは、簡単な2-Opt法を用います。2-Opt法は、まずランダムな経路から始めます。経路の中の2つの辺(edge)を選び、点の繋ぎ方を交換したときに距離が短くなれば経路を交換します。これを全ての組み合わせに対して実行する、というものです。
焼きなまし法 (Simulated Annealing)について
Simulated Annealing(以下SA)がどういうアルゴリズムか説明します。純粋な2-Opt法の問題は局所的最適解に陥ってしまうことでした。これは巡回セールスマン問題に限らず、あらゆる最適化問題での難点ですが、単にエネルギー状態(今回であれば経路の長さ)が低いほうに進むだけでは大域的最適解に至らず、局所的最適解に留まってしまうということが起こります。
そこで、SAではどうするかというと、計算の最初のうちは自由に振動できるようにします。詳しく言えば、経路を2-Opt法で交換した際、経路長が短くなれば交換しますが、経路長が長くなっても確率的に経路の交換をするようにします。ここが単なる2-Opt法と異なる点です。そしてイテレーションの終りの方では経路長が長くなる時に経路の交換を行う確率が低くなるようにします。イメージとしては、下図のような感じです。球は経路の状態を物体に例えたものです。
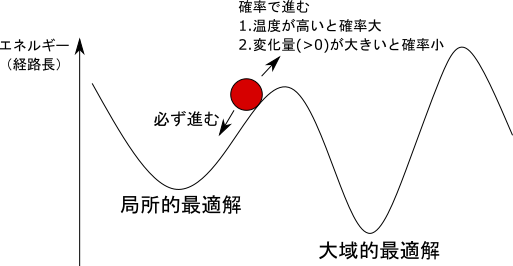
このSAでは「温度」というものを考えます。「温度」とは仮想的なもので、計算が進行すれば下がっていく変数を設定します。「温度低下」により、経路の状態は下図のように動きます。先ほどの話を「温度」を用いて言い換えれば、温度が高いときは経路長が長くなった時に経路を交換する確率が高いが、温度が低くなると、その確率は減少するということです。上のプログラムでは温度を指数関数的に減少させています。
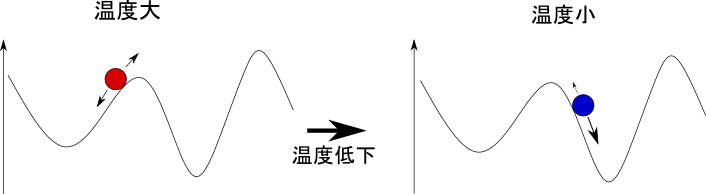
SAの名前が焼きなまし(Annealing)から来ているのはこれによります。温度が高いときはよく振動し、温度が下がるにつれて安定な状態へと落ち着くというのが焼きなましの手法に似ているからです。初期に振動をさせることで局所的最適解から抜けようということで、初期は解の振動が激しいものの、終りに近づくにつれて徐々に収束するような挙動をします。
コード
int seq=0; //シークエンス
int MAX_Iter=200;
int iteration;
float temp;
int NUM=50; //上限値
int count=0;
float[][] vertex_pos=new float[NUM][2];
int[] order_vertex; //頂点の順番
float[][] dist_mat; //距離行列
float total_dist;
float min_total_dist=100000;
int[] min_order_vertex;
void setup() {
size(500,500);
//frameRate(60);
background(255);
fill(0);
textSize(20);
textAlign(CENTER);
}
void draw() {
if(seq==0){
background(255);
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
stroke(0);
strokeWeight( 10 );
point(vertex_pos[i][0],vertex_pos[i][1]);
}
strokeWeight(1);
textAlign(LEFT);
text("Number of Points : "+count,20,140);
textAlign(CENTER);
text("Click the window",width/2,50);
text("Press ENTER to Calculate",width/2,80);
text("Press 'c' to Clear Points",width/2,110);
}else if(seq==1){
Calculate_setup();
seq+=1;
}else if(seq==2){
background(255);
temp=Temperature(iteration);
Calculate_2opt_method_with_Simulated_Annealing();
Disp_path();
total_dist=Calculate_total_dist();
if(total_dist<min_total_dist){
min_total_dist=total_dist;
min_order_vertex=order_vertex;
}
textAlign(LEFT);
text("Temp : "+ nf(temp,3,2),20,100);
text("Number of Points : "+count,20,140);
textAlign(CENTER);
text("Total Distance : "+ nf(total_dist,5,1),width/2,height-20);
iteration+=1;
text("Iteration : "+ iteration,width/2,50);
if(iteration>=MAX_Iter){
seq=3;
}
}else if(seq==3){
order_vertex=min_order_vertex;
Disp_path();
total_dist=Calculate_total_dist();
text("Min Total Distance : "+ nf(total_dist,5,1),width/2,height-20);
textAlign(LEFT);
text("Number of Points : "+count,20,80);
textAlign(CENTER);
text("Press ENTER to Calculate Again",width/2,50);
noLoop();
}
}
void mouseClicked() {
if(seq==0){
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(10);
point( mouseX, mouseY );
vertex_pos[count][0]=mouseX;
vertex_pos[count][1]=mouseY;
count+=1;
}else if(seq==3){
loop();
iteration=0;
seq=0;
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(10);
point( mouseX, mouseY );
vertex_pos[count][0]=mouseX;
vertex_pos[count][1]=mouseY;
count+=1;
}
}
void keyPressed() {
if ( key == 'c' ) {
if(seq==0 || seq==3){
background( 255 );
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++){
vertex_pos[i][0]=0;
vertex_pos[i][1]=0;
}
seq=0;
count=0;
iteration=0;
loop();
}
}else if(key == ENTER){
if(seq==0){
seq+=1;
}else if(seq==3){
iteration=0;
seq=1;
}
loop();
}
}
void Calculate_setup(){
order_vertex=Fisher_Yates_shuffle(count);
dist_mat=new float[count][count];
min_order_vertex=new int[count];
min_total_dist=100000;
//距離行列の計算
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
for(int j=0;j<count;j++){
if(i==j){
dist_mat[i][j]=0;
}else{
dist_mat[i][j]=sqrt(sq(vertex_pos[i][0]-vertex_pos[j][0])+sq(vertex_pos[i][1]-vertex_pos[j][1]));
}
}
}
Disp_path();
}
//2opt法の計算
void Calculate_2opt_method_with_Simulated_Annealing(){
for(int i=0;i<count-2;i++){
for(int j=i+2;j<count;j++){
float exchange_cost=Calculate_2opt_exchange_cost(i,j);
if(exchange_cost<0){
Swap_2opt(i,j);
}else{
float prob=Exchange_Probability(exchange_cost);
//println(prob);
if(random(0,1)<=prob){
Swap_2opt(i,j);
}
}
}
}
}
//頂点を交換した際のコストの変化量の計算
float Calculate_2opt_exchange_cost(int i,int j){
float dist_before=0;
float dist_after=0;
int j1;
if(j==count-1){
j1=0;
}else{
j1=j+1;
}
if(i!=0 || j1!=0){
float dist1=dist_mat[order_vertex[i]][order_vertex[i+1]];
float dist2=dist_mat[order_vertex[j]][order_vertex[j1]];
float dist3=dist_mat[order_vertex[i]][order_vertex[j]];
float dist4=dist_mat[order_vertex[i+1]][order_vertex[j1]];
dist_before=dist1+dist2;
dist_after=dist3+dist4;
}
return dist_after-dist_before;
}
//頂点番号の入れ替え
void Swap_2opt(int i,int j){
int tmp=order_vertex[i+1];
order_vertex[i+1]=order_vertex[j];
order_vertex[j]=tmp;
}
float Exchange_Probability(float exchange_cost){
return exp(-exchange_cost/temp);
}
float Temperature(int iteration){
return 100-pow(100,float(iteration)/MAX_Iter);
}
//経路の表示
void Disp_path(){
background(255);
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
stroke(0);
strokeWeight( 10 );
point(vertex_pos[i][0],vertex_pos[i][1]);
}
noFill();
strokeWeight(1);
beginShape();
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
vertex(vertex_pos[order_vertex[i]][0],vertex_pos[order_vertex[i]][1]);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
fill(0);
}
//総経路距離の計算
float Calculate_total_dist(){
float tmp_total_dist=0;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
if(i<count-1){
tmp_total_dist+=dist_mat[order_vertex[i]][order_vertex[i+1]];
}else{
tmp_total_dist+=dist_mat[order_vertex[i]][order_vertex[0]];
}
}
return tmp_total_dist;
}
int[] Fisher_Yates_shuffle(int number){
int[] tmp=new int[number];
for(int i=0;i<number;i++){
tmp[i]=i;
}
for(int i=0;i<number;i++){
int j=int(random(number));
int t=tmp[i];
tmp[i]=tmp[j];
tmp[j]=t;
}
return tmp;
}